Roman-era gold-covered baby mummy found in Akhmim, Egypt: an ancient marvel of archeology
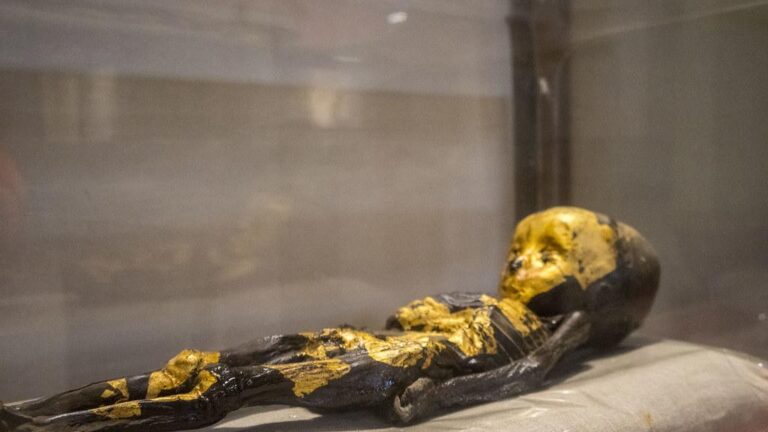

Meet the ‘Gold Dust Infant,’ an extraordinary find from the Roman period, believed to be an 8-month-old girl. This unique mummy, originally coated in shimmering gold dust, harbors a distinctive history of preservation and intriguing postmortem anomalies.
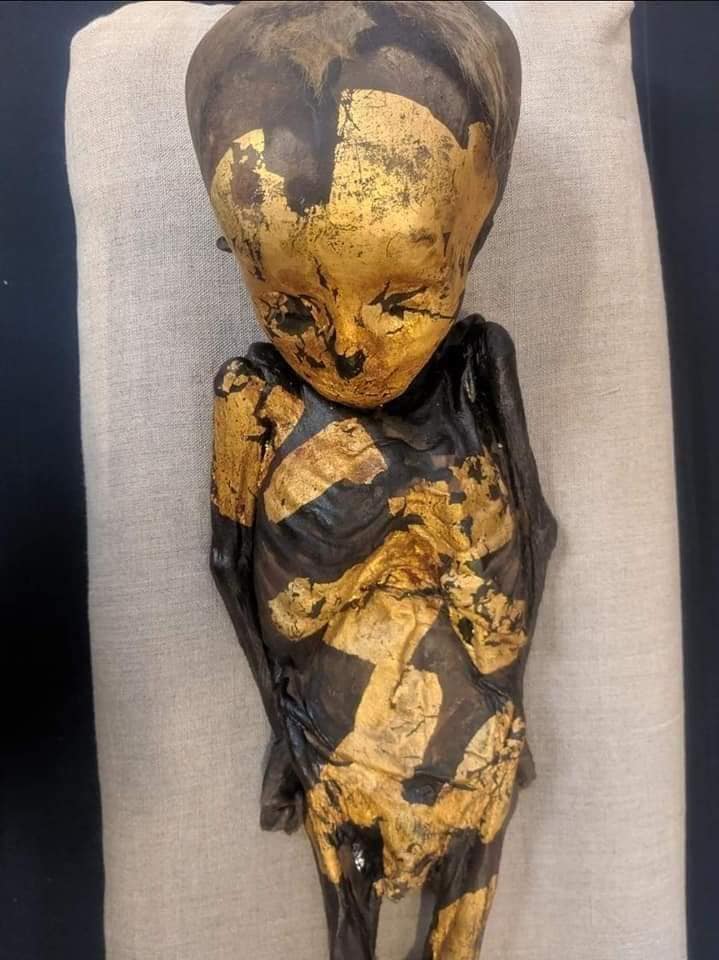
What sets this mummy apart is the unconventional approach taken during excerebration, a process typically ᴀssociated with the transnasal or foramen magnum routes. In this case, an artificial aperture was meticulously crafted in the skull, situated just behind the left ear and near the pars petrosum of the temporal bone. Notably, this cranial defect shows no signs of postmortem healing, indicating its posthumous origin.
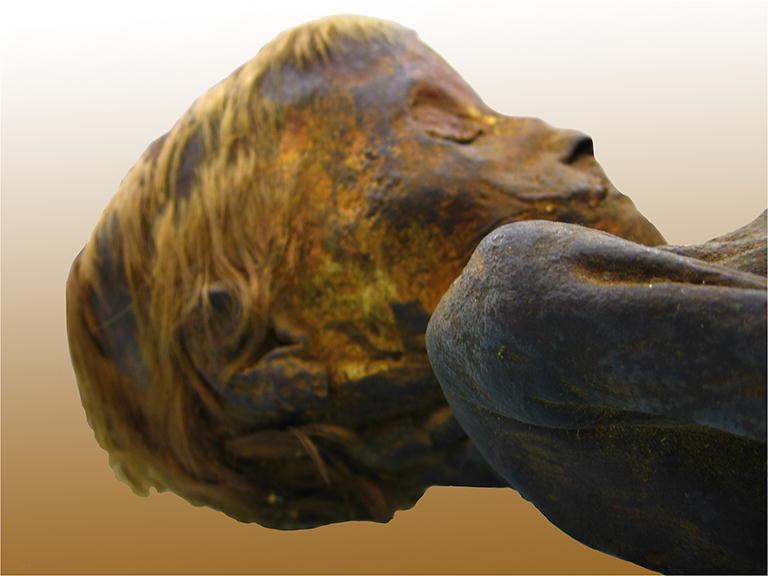

Upon unwrapping, remnants of the original wrapping material were discovered, with intriguing questions about when and why this elaborate burial was disturbed. Further examination revealed a missing third rib on the right side, with the sixth and seventh ribs oddly positioned, likely repositioned during the embalming process. The repositioned rib serves as a captivating piece of the puzzle, as it prevented the thorax from collapsing, in contrast to the abdomen.
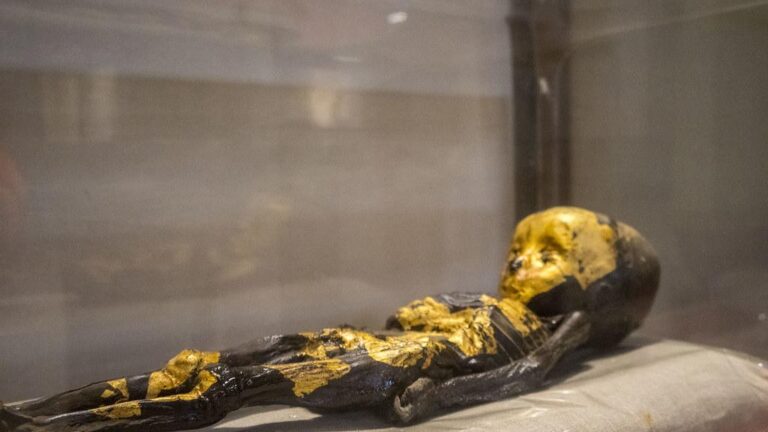

Adding to the mystery, the ‘Gold Dust Infant’ boasted naturally light-colored hair, possibly enhanced with henna. This captivating find not only offers a glimpse into ancient Egyptian burial practices but also raises tantalizing questions